The Differences Between Traditional And Self-Funded Health Plans: A Comprehensive Guide
The Differences Between Traditional and Self-Funded Health Plans: A Comprehensive Guide
As an employer, offering health insurance to your employees can be a great way to attract and retain top talent, improve productivity, and enhance your overall reputation. However, with the rising costs of healthcare and the complexity of the health insurance market, it can be challenging to determine which type of health plan is best for your business. In this article, we’ll break down the differences between traditional and self-funded health plans, helping you make an informed decision that suits your organization’s unique needs.
What are Traditional Health Plans?
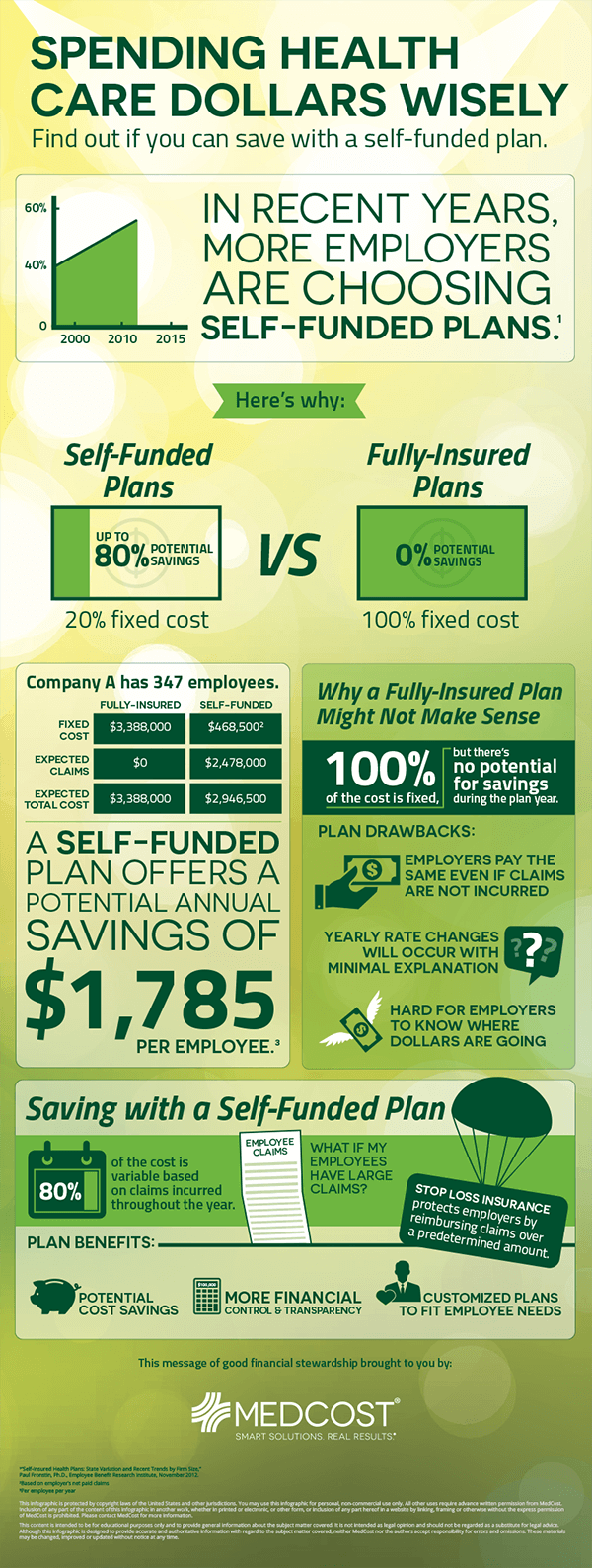
Traditional health plans, also known as fully insured plans, are the most common type of health insurance. In this model, you, as the employer, purchase a health insurance policy from an insurance company, such as UnitedHealthcare or Aetna. The insurance company assumes the financial risk of providing health benefits to your employees and their dependents. In exchange, you pay a premium to the insurance company, which is typically a fixed amount per employee per month.
Here are some key characteristics of traditional health plans:
- Predictable Costs: With a traditional plan, you know exactly how much you’ll pay each month for health insurance.
- Insurance Company Assumes Risk: The insurance company takes on the financial risk of providing health benefits, which means you won’t have to worry about unexpected medical claims.
- Limited Flexibility: Traditional plans often come with standardized benefit designs and limited opportunities for customization.
- Broker Assistance: Insurance brokers play a significant role in traditional plans, helping you choose a plan and negotiate rates.
What are Self-Funded Health Plans?
Self-funded health plans, also known as self-insured plans, are an alternative to traditional health insurance. In this model, you, as the employer, take on the financial responsibility of providing health benefits to your employees and their dependents. You set aside funds to pay for medical claims, and you may also purchase stop-loss insurance to protect against catastrophic claims.
Here are some key characteristics of self-funded health plans:
- Customization: Self-funded plans offer greater flexibility in terms of benefit design, allowing you to tailor your plan to your organization’s unique needs.
- Employer Assumes Risk: With a self-funded plan, you assume the financial risk of providing health benefits, which means you’ll need to budget for medical claims.
- Variable Costs: Self-funded plans have variable costs, as the amount you’ll pay for medical claims can fluctuate from month to month.
- Third-Party Administrator (TPA) Assistance: Self-funded plans often involve the use of a TPA, which helps you manage administrative tasks, such as claims processing and benefits administration.
Key Differences Between Traditional and Self-Funded Health Plans
When deciding between traditional and self-funded health plans, there are several key differences to consider:
- Cost Structure: Traditional plans involve paying a fixed premium to the insurance company each month, while self-funded plans require you to set aside funds to pay for medical claims.
- Risk Management: Traditional plans transfer the financial risk of providing health benefits to the insurance company, while self-funded plans require you to assume this risk.
- Flexibility: Self-funded plans offer greater flexibility in terms of benefit design, allowing you to create a plan that meets your organization’s unique needs.
- Administrative Responsibilities: Self-funded plans often involve greater administrative responsibilities, as you’ll need to manage tasks such as claims processing and benefits administration.
- Stop-Loss Insurance: Self-funded plans may involve purchasing stop-loss insurance to protect against catastrophic claims.
- Minimum Employer Contribution: Traditional plans typically require a minimum employer contribution, while self-funded plans do not.
- Eligibility Requirements: Traditional plans may have eligibility requirements, such as a minimum number of employees, while self-funded plans often have fewer restrictions.
- State and Local Taxes: Self-funded plans may be exempt from certain state and local taxes, such as premium taxes.
Advantages of Self-Funded Health Plans
Self-funded health plans offer several advantages, including:
- Customization: Self-funded plans allow you to tailor your plan to your organization’s unique needs and goals.
- Cost Savings: Self-funded plans can help you save money by eliminating administrative fees and profit margins associated with traditional plans.
- Increased Transparency: Self-funded plans often involve greater transparency, as you’ll have access to detailed claims data and administrative costs.
- Flexibility: Self-funded plans can be adapted to meet changing business needs and market conditions.
- Tax Benefits: Self-funded plans may be exempt from certain state and local taxes, such as premium taxes.
Disadvantages of Self-Funded Health Plans
Self-funded health plans also have some disadvantages, including:
- Assuming Financial Risk: Self-funded plans require you to assume the financial risk of providing health benefits, which can be challenging to budget for.
- Increased Administrative Responsibilities: Self-funded plans often involve greater administrative responsibilities, such as claims processing and benefits administration.
- Uncertainty Around Claim Costs: Self-funded plans can involve uncertainty around claim costs, as medical costs can fluctuate from month to month.
- Minimum Viable Population Size: Self-funded plans often require a minimum viable population size to be effective, which can be a challenge for smaller employers.
- Stop-Loss Insurance Costs: Self-funded plans may involve purchasing stop-loss insurance to protect against catastrophic claims, which can add additional costs.
Who is Best Suited for Self-Funded Health Plans?
Self-funded health plans are often best suited for organizations that:
- Have a Large Enrollment: Self-funded plans can be effective for organizations with a large enrollment, as this can help to spread risk and reduce administrative costs.
- Have a Stable Claims Experience: Self-funded plans can be beneficial for organizations with a stable claims experience, as this can help to reduce uncertainty around claim costs.
- Have a Strong Financial Position: Self-funded plans require a strong financial position to assume the financial risk of providing health benefits.
- Have a Willingness to Take on Administrative Responsibilities: Self-funded plans often involve greater administrative responsibilities, such as claims processing and benefits administration.
Who is Best Suited for Traditional Health Plans?
Traditional health plans are often best suited for organizations that:
- Have a Small Enrollment: Traditional plans can be more effective for smaller organizations, as they offer predictable costs and reduced administrative responsibilities.
- Have Limited Budget: Traditional plans can be beneficial for organizations with limited budgets, as they offer a predictable cost structure.
- Are Looking for a Simplified Process: Traditional plans often involve fewer administrative responsibilities, making them a simpler option for organizations.
- Are Willing to Sacrifice Customization: Traditional plans often involve standardized benefit designs and limited opportunities for customization.
Conclusion
When deciding between traditional and self-funded health plans, it’s essential to consider the unique needs and goals of your organization. While traditional plans offer predictable costs and reduced administrative responsibilities, self-funded plans offer customization, cost savings, and increased transparency. Ultimately, the choice between traditional and self-funded health plans will depend on your organization’s size, financial position, administrative capabilities, and willingness to assume risk.
We hope this article has provided a comprehensive guide to the differences between traditional and self-funded health plans. If you have any further questions or would like to discuss your organization’s specific needs, please don’t hesitate to reach out.
Comments
Post a Comment